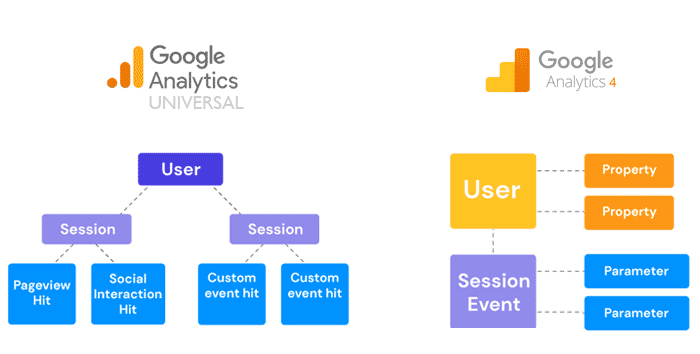
The key differences between Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Universal Analytics (UA) are as follows
1. Data Model:
- GA4: GA4 introduced a new event-based data model, where events are at the core of tracking and analysis. Events represent specific actions taken by users, such as pageviews, clicks, form submissions, video plays, and more. This allows for more flexibility in data collection and analysis, as businesses can define and track custom events that align with their specific goals and objectives.
- UA: UA uses a session-based data model, where a session is a collection of interactions that occur within a specific timeframe. The primary unit of measurement in UA is the session, and it tracks metrics like session duration, pageviews, and bounce rate.
2. Cross-Platform Tracking:
- GA4: GA4 is designed to track user interactions across various platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and offline interactions. It provides a more comprehensive view of user behavior by unifying data from different touchpoints. This cross-platform tracking capability allows businesses to understand how users engage with their brand across different devices and channels, enabling a more holistic analysis of the customer journey.
- UA: UA primarily focuses on tracking data from websites and has limited capabilities for tracking mobile apps or other platforms. It is primarily designed for web analytics and may require additional configurations or integrations to track data from different platforms.
3. User-Centric Measurement:
- GA4: GA4 places a stronger emphasis on individual user tracking and analysis. It introduces the User ID feature, which allows businesses to associate multiple sessions and interactions with a specific user. This enables tracking of user behavior across devices and platforms, providing a more complete understanding of the customer journey. The User ID feature can be particularly useful for businesses with a logged-in user base or those seeking to analyze user behavior across multiple devices.
- UA: UA primarily focuses on aggregated data and does not have built-in mechanisms for tracking individual users across devices without additional customization. User-centric analysis in UA often relies on cookies and anonymous identifiers, which may limit the ability to track users across sessions or devices.
4. Machine Learning and AI:
- GA4: GA4 incorporates advanced machine learning and AI capabilities to provide automated insights and predictive analytics. It can automatically identify trends, anomalies, and opportunities in the data without the need for manual analysis. For example, GA4 can alert businesses to significant changes in data, provide audience insights, predict user churn, and recommend optimizations based on user behavior patterns. These AI-driven features save time and help businesses make data-driven decisions more effectively.
- UA: UA has limited built-in machine learning and AI capabilities compared to GA4. While UA provides data visualization and reporting features, advanced analysis and predictive capabilities are more limited and often require manual data exploration and interpretation.
5. Reporting and Analysis:
- GA4: GA4 offers a more streamlined and user-friendly reporting interface compared to UA. It provides prebuilt reports and templates, such as engagement, retention, and conversion reports, which allow businesses to quickly access important metrics and insights. GA4 also includes the Exploration tool, which enables ad hoc analysis by dragging and dropping dimensions and metrics, making it easier to customize and explore data. The Analysis Hub in GA4 offers preconfigured analysis techniques, such as cohort analysis, path analysis, and segment overlap, providing more advanced analysis capabilities out of the box.
- UA: UA has a more complex reporting interface with separate sections for customization, such as goals, funnels, and segments. While UA offers a wide range of reporting options and customization possibilities, the interface can be overwhelming for users new to analytics or those seeking more streamlined reporting experiences.
6. Privacy and Data Control:
- GA4: GA4 introduces enhanced privacy and data control features to align with evolving privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. It includes options for data retention controls, allowing businesses to define how long they want to retain user data. GA4 also supports Consent Mode, which allows businesses to adjust data collection based on user consent preferences. Additionally, GA4 provides more transparency in data collection and processing, making it easier for businesses to comply with privacy regulations and provide transparency to users.
- UA: UA provides basic data control features, such as the ability to exclude specific IP addresses from being tracked, enable data sampling, and define data retention periods. However, stricter privacy regulations may require additional customization or configurations to comply fully.
These differences between GA4 and UA highlight the evolution of Google Analytics toward a more advanced and user-centric analytics platform. GA4 offers more flexibility, cross-platform tracking capabilities, advanced analysis tools, and enhanced privacy features compared to UA. Businesses are encouraged to consider migrating to GA4 to take advantage of its advanced features and align with the future direction of Google Analytics.